Comprehensive dental exam
What is involved in the comprehensive examination?
Medical History review:
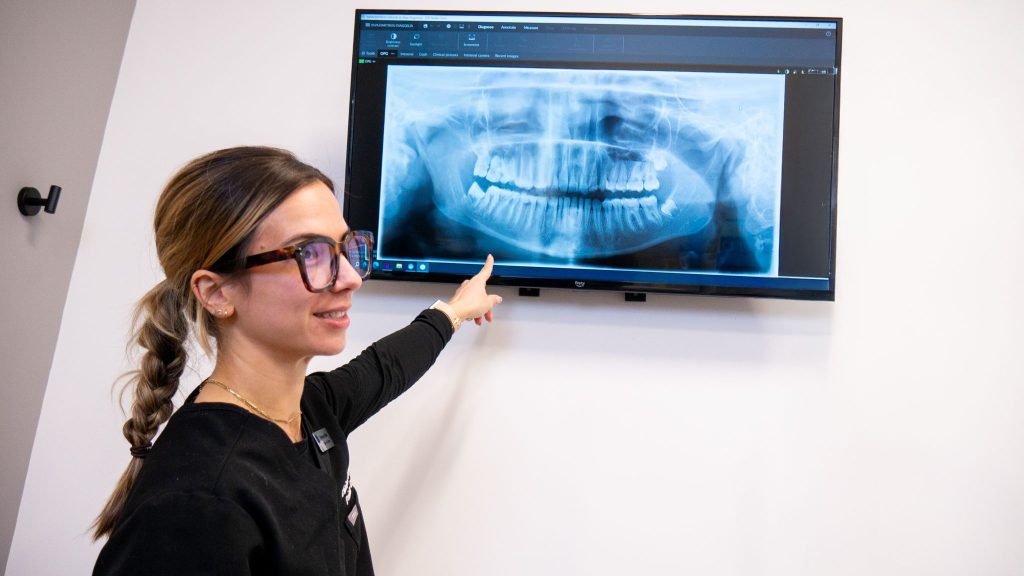
Digital X-Rays:
If appropriate for you, a full set of x-rays will be taken to help us detect and diagnose any issues that are not visible during a visual examination. With help of XRays, the dentist can detect the presence of cavities in between teeth or under existing fillings. These XRays can also reveal infections, impacted teeth, any bone loss or cysts and any other possible abnormalities in the oral cavity.
Digital XRays use up to 90% less radiation than traditional film X-rays, making them extremely safe for patients of all ages.
Visual examination:
The dentist will inspect your entire mouth thoroughly, including teeth, gums, tongue, cheeks, roof, and floor of the mouth.
Your teeth: We examine every tooth for possible damage, including cracks and chips that may cause discomfort. If you have fillings, crowns, bridges, implants, or other dental restorations, the dentist will evaluate their condition and integrity and detect decay or early signs of cavities.
Your gums: We examine the condition of your gums and identify signs of gum disease, such as bleeding or inflammation and check for periodontal pockets, which can lead to tooth and bone loss. Based on this screening, a complete periodontal exam may be recommended.
Your soft tissues: All the soft tissues of the mouth, including gums, tongue, cheeks, and lips, are examined for signs of oral diseases, such as oral cancer, infections, or lesions.
Your joints and bite (occlusion): We check your masticatory system including the position of your teeth and the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and look for signs of teeth grinding or clenching. This includes checking for issues such as crooked teeth, overbites, underbites, or malocclusion.
